GEMET keywords
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
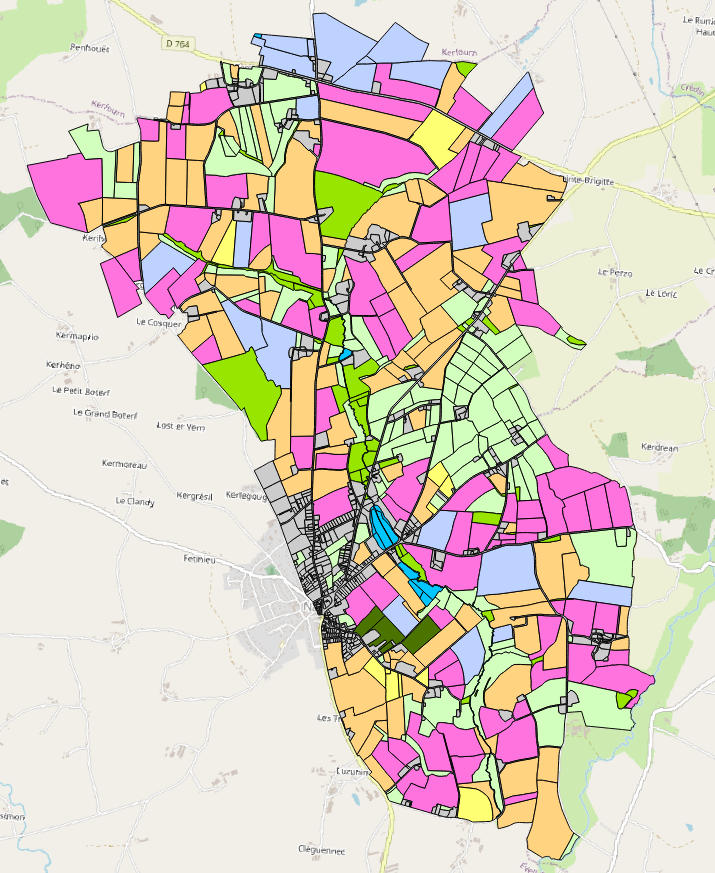
Occupation des sols 1995 du bassin versant du site de Naizin dans le Morbihan dans le cadre de l'Observatoire de Recherche en Environnement (ORE) AgrHyS d'INRAE. Le parcellaire est issu du cadastre de 2013. Les dessertes ont été redessinées à partir des orthophotos IGN de 2013 et le parcellaire a été découpé en fonction d’une zone tampon autour de ces dessertes. Les parcelles 2013 peuvent être découpées mais jamais regroupées. Toutes les entités géographiques élémentaires ont un identifiant unique sur l’ensemble des années. Champs de la table d’attribut : • ID_1995 : identifiant de la parcelle pour l’année 1995 • TYPE : code principal de l’occupation des sols • S_TYPE : code secondaire de l’occupation des sols La nomenclature de ces codes des types et sous-types a été définie dans le programme ANR-12-AGRO-0005 MOSAIC : https://anr.fr/Projet-ANR-12-AGRO-0005. Leurs descriptions peuvent être télécharger ici : https://geosas.fr/metadata/ore/xls/legendes_osol_naizin.xlsx. Les occupations des sols sont issues de photo-interprétation dans le cadre du programme CORMORAN (Cheverry et al., 1998). Les limites des parcelles ont été mises en concordance avec le parcellaire de 2013.
-
L’ouverture des barrages va considérablement impacter le fonctionnement des populations piscicoles de la Sélune. Le rétablissement de la continuité écologique du fleuve modifiera les flux populationnels en autorisant la remontée plus en amont de certaines espèces amphihalines et le déplacement d'autres espèces vers l'aval et en amont des barrages. Depuis maintenant de nombreuses années, dans le cadre de l'ORE DiaPFC (Observatoire de Recherche en Environnement Poissons Diadromes dans les Fleuves Côtiers), du SOERE OLA (Système d'Observation et d'Expérmentation pour la recherche en environnement Observatoire des lacs alpins) ou du Pôle OFB-INRAE-Institut Agro-UPPA, différentes unités INRAE (U3E, l'UMR ECOBIOP et l'UMR CARRTEL) et OFB (DRAS) prélèvent des échantillons sur de nombreux spécimens aquatiques. Ces échantillons, généralement otolithes, écailles et/ou nageoires, servent ensuite à la communauté scientifique pour effectuer différentes analyses et recherches. Ces prélèvements ont également lieu dans le cadre de l’observatoire Sélune. Labélisé Centre de Ressources Biologiques (CRB) par le GIS IBISA, Colisa fait partie du pilier environnement BRC4Env (réseau des Centres de Ressources Biologiques pour l'Environnement) de l'infrastructure RARe. Notre catalogue référence ces différents échantillons de tissus durs et propose un module permettant d'effectuer des requêtes sur notre base de données et de sélectionner les types de données susceptibles de vous intéresser. Vous pourrez par la suite exporter ces données. Ce jeu de données ne présente, en l’occurrence, aucune donnée spécifique mais permet le lien vers l'application COLISA (COLlection of Ichtyological SAmple : Collection d'échantillons ichtyologiques) permettant le stockage des échantillons prélevés. L'application COLISA nécessite la création d'un compte utilisateur pour l'accès à la totalité de la collection.
-

Le cours amont de la Sélune n'est pas accessible aux poissons migrateurs du fait des deux barrages hydroélectriques. Les lamproies sont bloquées à une quinzaine de kilomètres de la mer par le premier barrage infranchissable de la Roche qui boit. La méthode utilisée pour échantillonner les lamproies est celle mise au point par Lasne et al. (2010) permettant de prélever plus efficacement les individus de très petite taille que par pêche électrique. La méthode s’appuie sur l’utilisation d’un outil dérivé du filet de Surber, permettant de prélever les ammocètes de façon standardisée. Cette enceinte permet de réaliser des prélèvements ponctuels, à la manière des EPA. La réalisation d’un point de prélèvement se déroule en plusieurs étapes. Après avoir localisé un microhabitat favorable, une caisse est enfouie dans le substrat jusqu’à une profondeur d’environ 15 cm. L’opérateur prélève alors le substrat et le dépose dans le filet. La colonne d’eau dans la caisse est filtrée et les sédiments dans le filet déposés sur un tamis afin de récupérer toutes les ammocètes. Ces dernières sont mesurées et des prélèvements génétiques sont effectués lorsque leur taille le permet. Un total de 30 prélèvements maximum est effectué par station. Ce tableau contient les données individuelles sur les lamproies capturées selon les années d'étude 2013, 2015, 2019 et 2021.
-
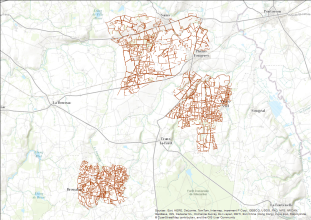
Cadre: carte de l'occupation du site C de pleine-Fougères (Zone Atelier Armorique) en 2007 Programmme: ECCO PNBC Date du vol: 1974
-
Relevés exhaustifs de la flore des bords de champs des 3 mini-réseaux bocagers de la Zone Atelier Armorique à Pleine-Fougères. Protocole: placé le long d'une haie, sur un tronçon homogène; coefficient d'abondance-dominance des espèces (dans certains cas transect de 25m sur la longueur ou sur la totalité de la haie).
-

Image satellite Quickbird acquise dans le cadre du programme Zone Atelier. Bandes multi-spectrales et panchromatique Qualité d'image mauvaise par endroit (brume)
-
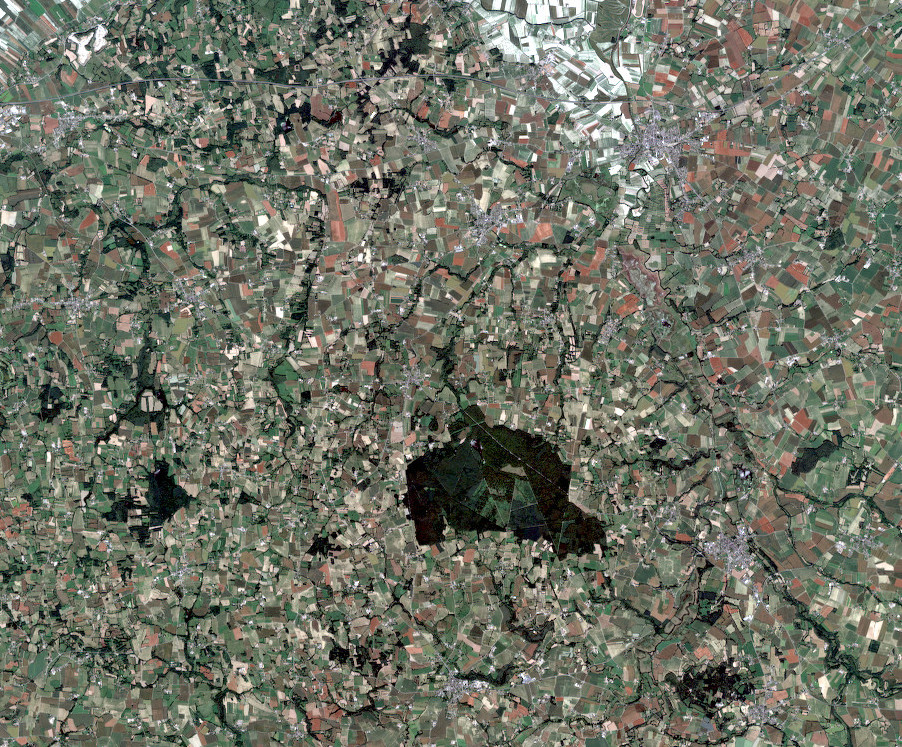

Image satellite Pléiades acquise dans le cadre du dispositif KALIDEOS Bretagne Acquisition le 23/06/2018 Le produit est protégé par des droits de diffusion. Il est disponible et téléchargeable sur le site suivant: https://bretagne.kalideos.fr/drupal/fr/mapshup_page Il est nécessaire de s'inscrire et avoir un compte pour télécharger les données KALIDEOS et il suffit de décrire son besoin (visualisation de données satellites récentes pour des applications en écologie par ex).
-

Objectif : Etude de l’effet de l’hétérogénéité de la mosaïque des cultures sur la biodiversité et les services écosystémiques Protocole : Occupation du sol réalisée par inventaire terrain Article de référence : à venir Programme de Recherche : ERA-Net BiodivERsA, Farmland
-

Occupation des sols 2012 du bassin versant du site de Naizin dans le Morbihan dans le cadre de l'Observatoire de Recherche en Environnement (ORE) AgrHyS d'INRAE. Le parcellaire est issu du cadastre de 2013. Les dessertes ont été redessinées à partir des orthophotos IGN de 2013 et le parcellaire a été découpé en fonction d’une zone tampon autour de ces dessertes. Les parcelles 2013 peuvent être découpées mais jamais regroupées. Toutes les entités géographiques élémentaires ont un identifiant unique sur l’ensemble des années. Champs de la table d’attribut : • ID_2012 : identifiant de la parcelle pour l’année 2012 • TYPE_12 : code principal de l’occupation des sols • S_TYPE_12 : code secondaire de l’occupation des sols • NUM_ILOT : identifiant numérique et non significatif par îlot du RPG 2012 • CODE_GROUP : code des cultures de l’îlot regroupées du RPG 2012 La nomenclature de ces codes des types et sous-types a été définie dans le programme ANR-12-AGRO-0005 MOSAIC : https://anr.fr/Projet-ANR-12-AGRO-0005. Leurs descriptions peuvent être télécharger ici : https://geosas.fr/metadata/ore/xls/legendes_osol_naizin.xlsx. Les occupations des sols sont issues des données par ilot du Registre Parcellaire Graphique (RPG) de l’année 2012. Les limites des parcelles ont été mises en concordance avec le parcellaire de 2013.
-
AgrHyS est un Observatoire de Recherche en Environnement (ORE) labellise par le Ministere de la Recherche en 2002, et un des observatoires de l'Infrastructure de Recherche nationale et distribuee OZCAR (Observatoires de la Zone Critique, Applications, Recherche) labellisee par le Ministere de la Recherche en 2017. Il est géré par L'INRA (UMRSAS à Rennes). Il a pour objectif d’étudier les temps de réponse des flux hydrogeochimiques à l'évolution des agro-hydrosystemes. Il étudie en particulier les agro-hydrosystèmes de milieux tempérés humides, dominés par une activité de polyculture-élevage.
 OSURIS
OSURIS